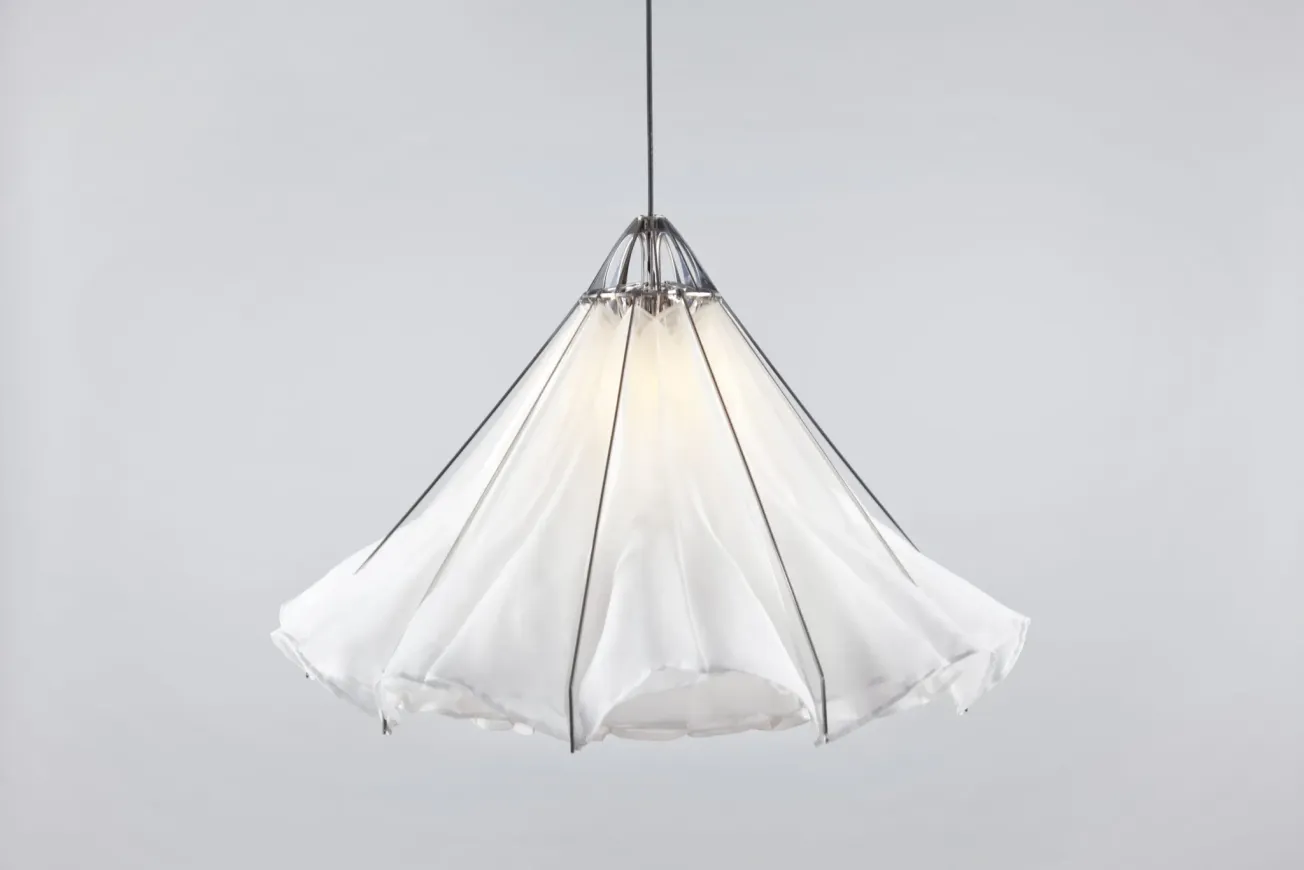
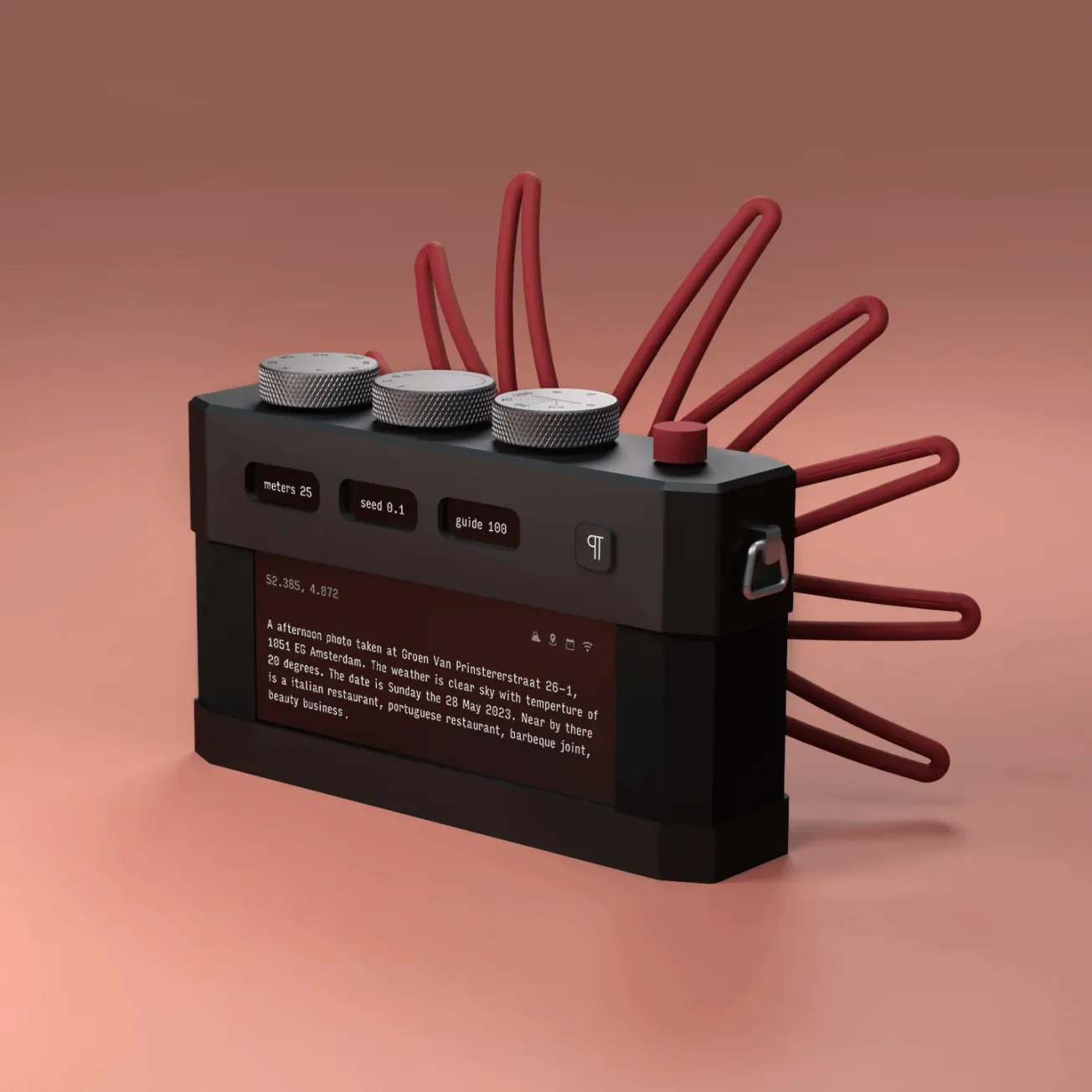
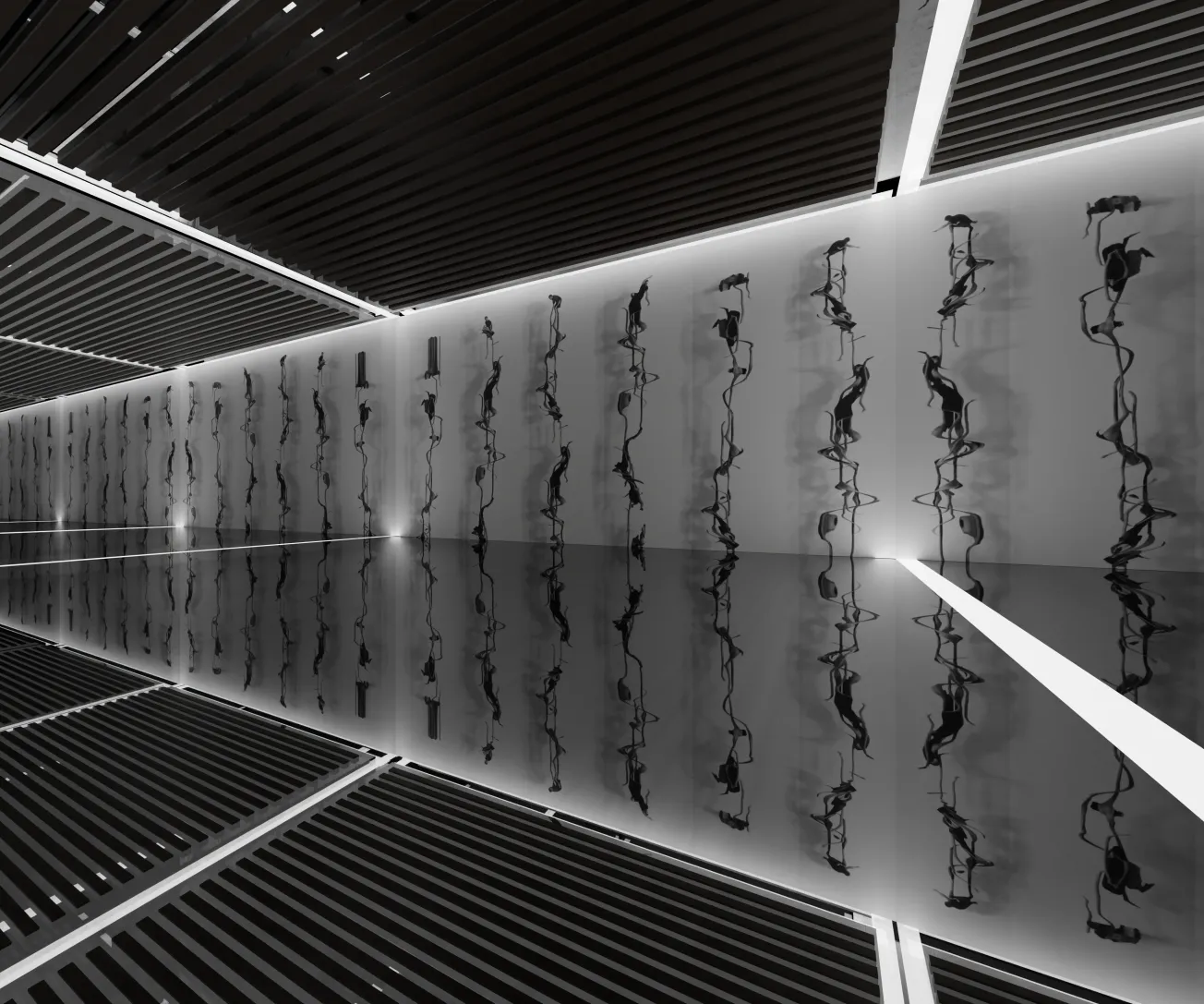
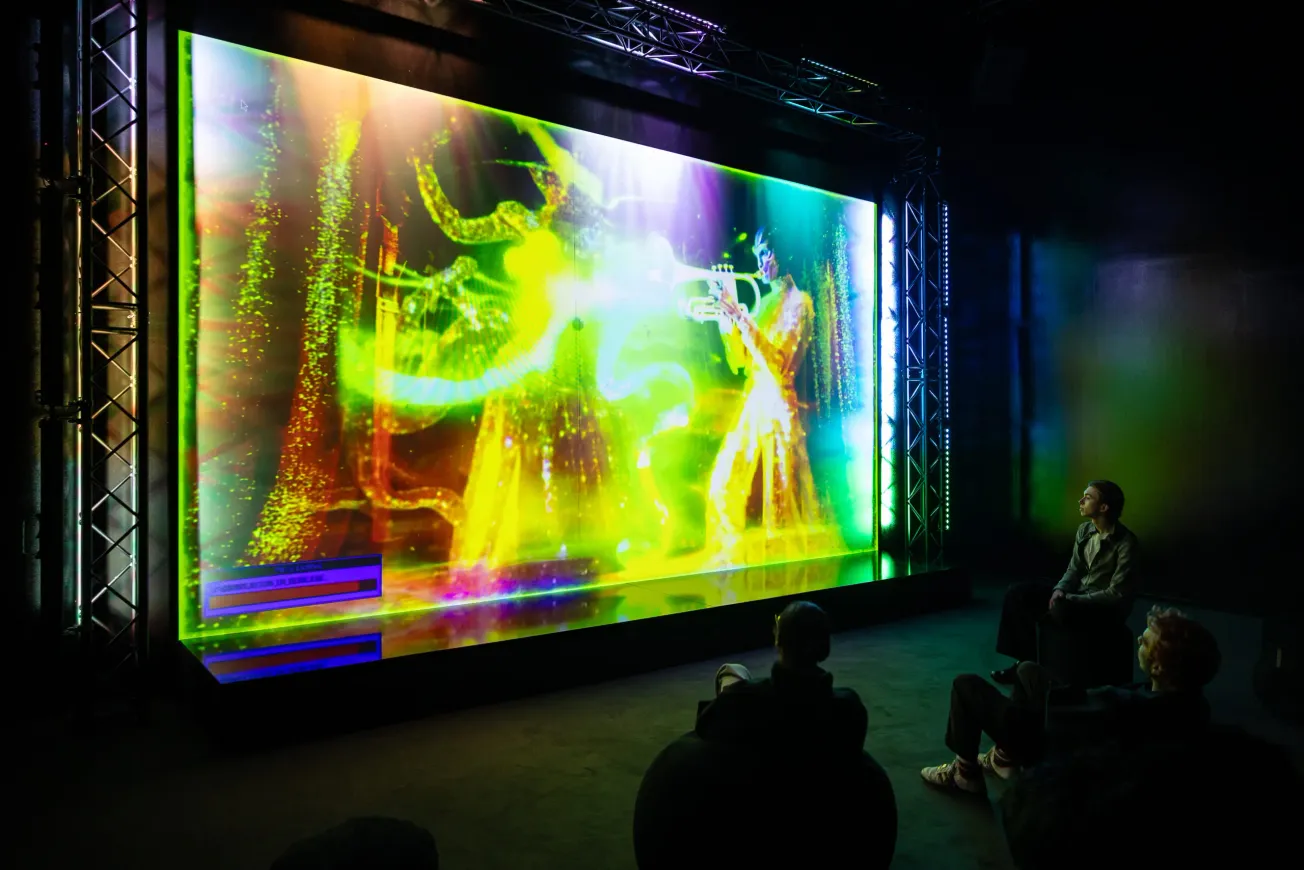
Fueled by the growing accessibility and affordability of fabrication, visualization, and production technologies, creative processes and practices have been rapidly evolving and transforming. From democratizing creative opportunities to enhancing efficiencies and productivity, these advancements are leading to both new forms of exploration and experimentation as well as new and alternate modes of making.
One of the most significant impacts of accessible technology is the democratization of creative opportunities. In the past, access to expensive equipment and software was limited to well-funded studios and firms. However, with the proliferation of affordable tools like 3D printers, laser cutters, and digital design software, individuals and small studios now have the ability to experiment, explore, design, and create with unprecedented ease. This democratization has leveled the playing field, allowing a more diverse range of voices and perspectives to enter the creative sphere.
Moreover, these technological advancements are increasing efficiencies and productivity within creative studios. Tasks that once required significant time and resources can now be completed in a fraction of the time, thanks to automation and digital workflows. For example, 3D modeling software enables designers to quickly iterate on their designs, while digital fabrication tools allow for rapid prototyping and iteration. As a result, creative studios can take on more projects and deliver high-quality work with greater speed and precision.
Accessible technologies are expanding exploratory and experimental capabilities within creative studios. Artists and designers can now push the boundaries of their craft by experimenting with new materials, techniques, and processes. Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies, for instance, offer immersive platforms for artistic expression, allowing creators to explore new forms of storytelling and interactive experiences. Additionally, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) are opening up new possibilities for generative art and design, where algorithms play an active role in the creative process. All of these can be done in one’s own studio without the need to outsource to businesses or partner with larger firms.
Another significant impact of accessible technology is the facilitation of collaboration and connectivity. Creative studios can now collaborate with artists, designers, and technologists from around the world in real-time, thanks to digital communication tools and cloud-based collaboration platforms. This interconnectedness fosters a culture of exchange and cross-pollination, where ideas can flow freely across disciplines and geographical boundaries. As a result, creative studios are able to leverage diverse perspectives and expertise to tackle complex challenges and push the boundaries of innovation.
Accessible technology is enabling the integration of traditional and emergent modes of making. While digital fabrication tools enable the production of intricate and complex designs, traditional craft techniques add depth and richness to the creative process. Many studios are embracing a hybrid approach, combining the precision of digital tools with the tactile qualities of handcrafted materials. This synthesis of old and new creates opportunities for unique and compelling works that bridge the gap between past and present.
As technology continues to evolve and become even more accessible, creative studios continue to embrace, adopt, adapt, and hack new tools and methodologies, leading to previously unimaginable results. In this rapidly changing terrain, the future of creative studios filled with endless possibilities for exploration, experimentation, and collaboration could lead to entirely new domains in creative practice.