As society's focus on sustainability and environmental responsibility grows, innovative materials and construction techniques are emerging with immense opportunity for positive impact in the construction industry. One such sustainable innovation developed by students, a number of years ago, at the Institute for Advanced Architecture of Catalonia (IAAC) is the Hydro-Ceramic Brick. Perhaps its time to revisit this technique?
The construction industry has long been a vital pillar of human civilization, responsible for building the structures that shape our cities and communities. However, the environmental consequences of traditional construction methods have raised concerns in recent years. The excessive use of energy and raw materials and the generation of substantial waste have been significant contributors to environmental degradation. Recognizing the need for change, the construction sector has been embracing innovation as it strives to align with the principles of sustainability. The Hydro-Ceramic Brick is a promising creation that could provide a tangible solution to address some of the industry's most pressing challenges.
Hydro-Ceramic Bricks are not your typical construction material. These bricks are designed to have an exceptional capacity to absorb and store water. This ability to hold moisture makes them invaluable in addressing two major issues in construction: temperature regulation and environmental impact.
One of the most remarkable features of Hydro-Ceramic Bricks is their capacity to help regulate temperature. By absorbing and storing water, these bricks serve as a natural coolant. When exposed to sunlight or warm environments, the bricks release the stored water slowly, creating a cooling effect in their vicinity. This has substantial implications for reducing the need for energy-intensive air conditioning in buildings, particularly in regions with hot climates. By incorporating Hydro-Ceramic Bricks into construction, architects and builders can create more energy-efficient structures. This innovative material contributes to the reduction of energy consumption, which is a pivotal step towards a greener and more sustainable construction industry.
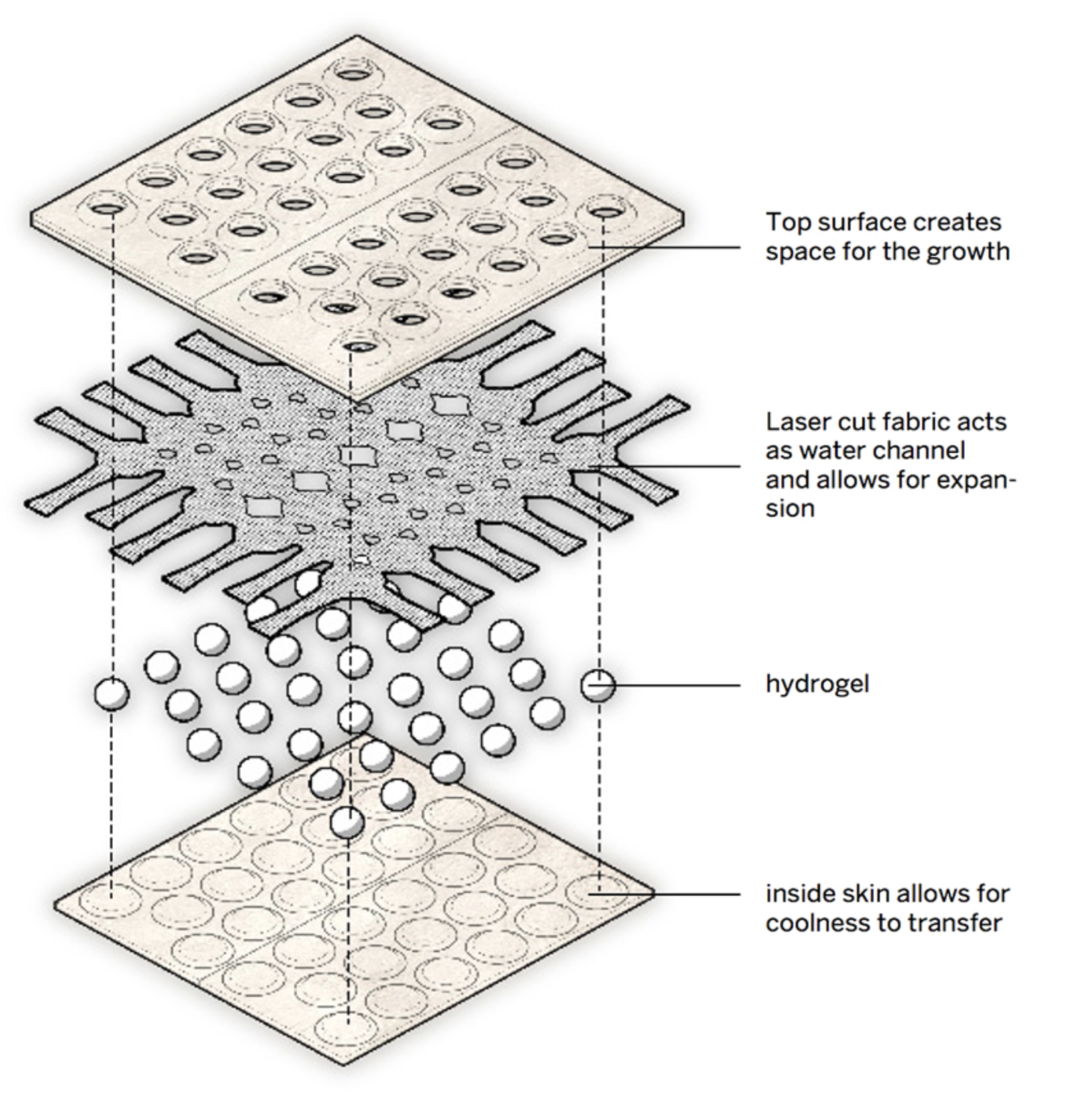
Traditional bricks and construction materials often have a substantial environmental footprint due to the energy-intensive processes involved in their manufacturing. Hydro-Ceramic Bricks, on the other hand, take a different approach. Their production process is more sustainable, with a reduced carbon footprint. Additionally, the cooling effect of these bricks can lead to energy savings in the long run. Moreover, the ability to absorb and store rainwater offers a practical solution for water management in urban areas. Hydro-Ceramic Bricks can reduce runoff during heavy rainfall, lessening the burden on stormwater drainage systems. This feature contributes to minimizing flooding in urban environments and preventing soil erosion, making them a vital component of sustainable urban planning.
The potential applications of Hydro-Ceramic Bricks are relatively vast, and their advantages are manifold, with opportunities for significant impact in a number of areas, including:
- Sustainable Housing: Sustainable housing is a growing trend in modern construction. Hydro-Ceramic Bricks can be used in residential buildings to enhance energy efficiency, reduce cooling costs, and create more comfortable living spaces. The cooling effect is particularly beneficial in regions with high temperatures.
- Green Roofs and Walls: The ability to absorb and release moisture makes Hydro-Ceramic Bricks ideal for green roofs and walls. These structures not only improve the aesthetic appeal of urban environments but also contribute to temperature regulation and air quality.
- Water Management: Hydro-Ceramic Bricks can play a pivotal role in water management, particularly in urban areas with limited green spaces. They assist in preventing flooding, minimizing runoff, and enhancing water conservation efforts.
- Sustainable Urban Planning: In the broader context of sustainable urban planning, Hydro-Ceramic Bricks offer a versatile solution. They can be used in public spaces, sidewalks, and streets to help maintain a cooler urban environment while reducing the strain on energy resources.
As the construction industry undergoes a transformation, the integration of innovative materials like Hydro-Ceramic Bricks represents a significant step towards sustainability. This shift not only addresses the environmental concerns associated with traditional construction but also sets a new standard for innovation in the field.
The adoption of such sustainable technologies is likely to continue growing as societies and governments worldwide prioritize environmental responsibility. The construction sector is adapting to meet these changing expectations, and Hydro-Ceramic Bricks exemplify the kind of forward-thinking solutions that can shape the industry's future.
While Hydro-Ceramic Bricks offer an array of benefits and innovative features, there are also challenges and considerations to be mindful of. As with any emerging technology, the successful integration of Hydro-Ceramic Bricks into the construction industry may require overcoming certain hurdles, including cost, the need for trained experts, regulatory compliance, and maintenance.
The initial cost of adopting new materials and technologies can be a significant barrier. Hydro-Ceramic Bricks may be more expensive than traditional bricks, but the long-term energy savings and environmental benefits can offset this cost. Builders, architects, and construction professionals may need specialized training to work with these innovative materials effectively. This necessitates an investment in education and skills development within the industry. Of course, the existing building codes and regulations may need to be updated to accommodate the use of Hydro-Ceramic Bricks and other sustainable construction materials. This may involve collaboration between the construction sector and government bodies. And the long-term durability of Hydro-Ceramic Bricks and their maintenance requirements should be carefully considered. Ensuring that they withstand environmental conditions and continue to function effectively over time is crucial.
Hydro-Ceramic Bricks could offer a useful step forward in the construction industry's pursuit of sustainability and innovation. These bricks, with their cooling capabilities and water management features, could transform the way we build and interact with our environment. The impact they can have on energy efficiency, water conservation, and urban planning underscores their potential to revolutionize construction practices.
As the world grapples with the climate crisis and environmental conservation, technologies like Hydro-Ceramic Bricks serve as beacons of hope and possibility. They embody the fusion of creative technology and societal needs, offering a glimpse into a future where our built environment becomes more harmonious with the natural world. The journey towards sustainable innovation in construction is well underway, and Hydro-Ceramic Bricks can be a useful tool in building a greener and more responsible future.
In the rapidly changing landscape of construction, the adoption of innovative materials is not merely an option; it is an imperative step towards a more sustainable and environmentally responsible future. The impact of these bricks extends far beyond construction sites; they hold the potential to transform our cities, our lifestyles, and our planet for the better.
Hydroceramics was developed by Akanksha Rathee, Elena Mitrofanova, and Pongtida Santayanon in Studio Digital Matter: Intelligent Construction, Master of Advanced Architecture at the Institute for Advanced Architecture of Catalonia (IAAC). The project was supported by Senior faculty Areti Markopoulou, Faculty assistant Alexandre Dubor and Assistant Moritz Belge.





